Quantum optics
From SMOSwiki
(Created page with "== Two photon interference == The interference of light was first studied by Thomas Young with his famous double slit experiment. This experiment showed first-order interference…")
Latest revision as of 13:41, 30 December 2010
Two photon interference
The interference of light was first studied by Thomas Young with his famous double slit experiment. This experiment showed first-order interference. Showed second-order interference of light and the first time experiment is by Hanbury Brown and Twiss using an intensity interferometer.[1]
Another type of interferometer which use the photon pairs from the spontaneous parametric down-conversion(SPDC) was built and used to show the quantum nature of light in 1987, which is called the 'Hong-Ou-Mandel dip' experiment.[2]
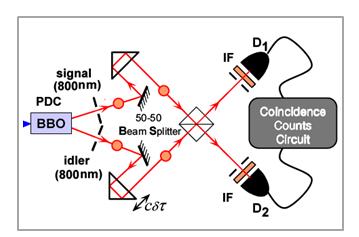
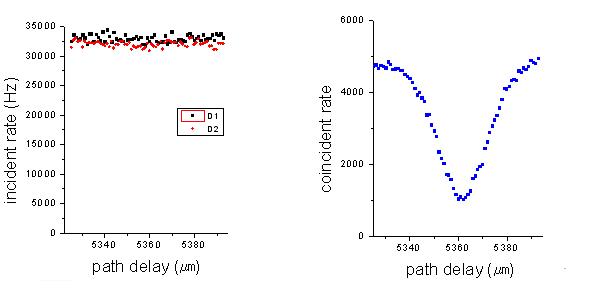
As shown in Fig.1, Generation of a photon pair is realized via parametric down conversion.Two photons where overlapped on a beam splitter spatially and temporally. The coincidence counts dropped down when the path lengths of the photons became identical.(Fig.2)
- ↑ R.Hanbury Brown and Twiss, Nature (London) 177, 27-32 (1956)
- ↑ CK Hong, ZY Ou, L Mandel, Phys. Rev. Lett 59, 2044 (1987))url
Photon bunching
In recent years, there is an interesting subject of the study of the thermal nature in the process of spontaneous parametric down-conversion (SPDC)[1][2]. Since in this process photons from a pump laser beams are randomly converted into pairs of photons at lower frequency. Bunched light consists of a stream of photons with the photons all clumped together in bunches. In 1987, Yurke and Potasek have investigated the thermal nature of the field in one arm of a SPDC source)[3]. We will measure the photon statistics of weak light pulse emitted in the process of pulsed parametric down-conversion.
Fig.3 is the experimental setup